
- Diploma prepared: Polytech Marseille engineer, specializing in Industrial and Computer Engineering.
- Average number of students in a class: 45 (FISE)
- Student profiles on entry: PEIP, CPGE, DUT/BUT, Licence, Master1
- Fields of study : Industrial Engineering, Computer Science, Automatics
- Options: Initial training (FI), Continuing training (FC), Professionalization contract (CP)
- Campus : Château-Gombert (Saint Jérôme)
Purpose of the program
The aim of this program is to train professional engineers specializing in the scientific organization, design, implementation and operation of systems for the production, supply and distribution of goods and services. The skills developed during the course give future engineers the ability to coherently combine the sciences of management, production engineering, computer science and automation.
At the end of their training, Industrial Engineering and Computer Science engineers will have acquired the following professional skills: (1) Managing an industrial project, (2) Managing industrial production, (3) Managing teams, technical and economic resources, (4) Designing, specifying and deploying an industrial production system and, (5) Designing, specifying and deploying an industrial information system.
Student testimonials


Ma formation dans la filière Génie Industriel et Informatique à Polytech Marseille a été une expérience captivante alliant l'informatique et l'industrie. Grâce à l'approche multidisciplinaire de la filière GII, j'ai appris à travailler efficacement au sein d'équipes pluridisciplinaires et à relever des défis complexes. J'ai développé des compétences en gestion de projet, indispensables pour mener à bien des projets industriels d'envergure. L'équilibre entre cours théoriques et pratiques a renforcé ma compréhension des concepts et stimulé mon esprit analytique, ma résolution de problèmes et ma créativité. En résumé, la filière GII de Polytech Marseille m'a préparé à une carrière d'ingénieure polyvalente, prête à relever les défis du secteur industriel.


Au-delà des compétences techniques de gestion et de conception des systèmes industriels développées grâce à ma formation d'ingénieur à Polytech Marseille - Génie Industriel et Informatique, le double diplôme en management de l’IAE m'a donné une compréhension approfondie de la dimension commerciale et managériale d'une entreprise. Cette combinaison très recherchée de compétences sur le marché du travail, incluant de la gestion de projet, la stratégie d'entreprise et l’analyse financière, m'a permis de devenir un ingénieur polyvalent, capable de mener des projets techniques et appréhender les enjeux économiques et managériaux. Aujourd’hui en contrat d’apprentissage dans le secteur de l’énergie, je me forme et contribue, au quotidien, à décarboner la production électrique.
-
3rd year
Semester 5
- UE - Language & SHEJS (Human, economic, legal and social sciences) 1
- EU - Engineering tools 1
- UE - Task organization
- UE - Basic automation for engineers
- EU - Basic engineering computing
Semester 6
- UE - Language & SHEJS 2
- UE - Engineering Tools 2
- UE - Process and Systems Modeling
- UE - Control and Regulation
- UE - Data Access and Representation
- UE - Company Discovery Internship
The aim of the SDE (Stage de Découverte de l'Entreprise) internship is to introduce third-year students to the world of work and business. It lasts a minimum of four weeks, and can be carried out within the framework of an agreement or an employment contract, in France or abroad.
-
4th year
Semester 7
- UE - Language & SHEJS 3
- UE - Industrial Systems Design
- UE - Automation for Production
- UE - Software Development
- UE - Technical Realization 1
Semester 8
- UE - Language & SHEJS 4
- UE - Operational Production Management
- UE - Dominant Automatics: Identification and Advanced Control
- UE - Computer Science: Computing for the IoT
- UE - Technical Realization 2
- UE - Initiation to Research Internship (SIR)
During semesters S8 and S9, students choose a major (Automatic Control or Computer Science).
The SIR is carried out in an international research laboratory at a university in a foreign country. This twelve-week internship validates the international mobility requirement for student engineers. -
5th year
Semester 9
- UE - Language & SHEJS 5
- UE - Operational Excellence
- UE - Dominant Automatique: Advanced Control for Renewable Energy Systems and Robotics
- UE - Computer Science: Methods and Tools for Decision Support
Semester 10
UE - Industrial Development Internship
The SVI (Stage de Valorisation Industrielle) internship at the end of the fifth year is entirely dedicated to putting students into professional situations, and is the necessary complement to their training in the corporate world. It lasts a compulsory minimum of seventeen weeks.
-
Double curriculum
Double curriculum Master 2 in General Management at IAE
During the 5th year, engineering students can follow a double curriculum to obtain a double engineer-manager qualification recognized by a double diploma: the engineering diploma from Polytech Marseille GII and the Master 2 in General Management from the Institut d'Administration des Entreprises (IAE).
Double Master's research curriculum
During the 5th year, engineering students wishing to continue their studies towards a doctorate can follow a double curriculum to obtain a double qualification in Engineering-Research recognized by a double diploma: the engineering diploma from Polytech Marseille GII and the Master 2 EEA from Aix-Marseille University.
-
Further studies
Once you've obtained your Industrial and Computer Engineering diploma, you have a wide range of options for further study:
- Specialized Masters recognized by the Conférence des Grandes Écoles (Bac+6)
- Master 2 in General Management from IAE Aix-Marseille University
- Toulouse Master's degree
- Doctoral theses
Teaching environment
The course's project-based pedagogy (Practical Teaching, Micro-Projects, Technical Realization Projects, End-of-Study Projects) confronts student engineers with problems of increasing complexity over the course of the semesters, culminating in professional issues directly related to industry.
To make it easier for students to enter the workforce and develop their entrepreneurial spirit while providing theoretical training, Polytech Marseille offers students project-based teaching, internships and the possibility of a professionalization contract as part of their engineering curriculum.
-
Professional integration
As numerous studies and surveys have shown, France has a shortage of engineers, particularly in the field of Industrial Engineering. In line with the development of the industry of the future (Industry 4.0), the Industrial Engineering and Computer Science specialization offers a modern and relevant vision of the engineering profession, and the engineers who graduate from it are positioned in all industrial and economic sectors, whether in large groups or in the SME-SMIs that are sources of numerous jobs.
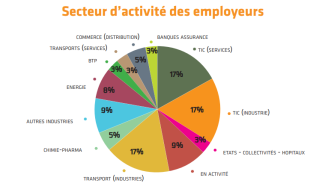 Employer sector GII
Employer sector GII- Banking & Insurance: 3% (Insurance)
- ICT (Services ): 17%
- ICT (Industry): 17
- Governments - Public authorities - Hospitals: 3%
- Active: 9% Transport (Industry)
- Transport (Industry): 17
- Chemicals-Pharmaceuticals: 5% Other industries
- Other industries 9%
- Energy: 8% Construction
- BUILDING & PUBLIC WORKS: 3%
- Transport (services): 3%
- Trade (distribution): 5% Other industries: 5% Other industries: 5% Other industries: 5% Other industries: 5% Other industries: 5% Other industries
-
Examples of graduate employers
ABB | ABC Automation | ACCENTURE | ACTEMIUM | AIRBUS | AIRBUS ATLANTIC | AIRBUS HELICOPTERS | ASSYSTEM EOS | ATOS |ATOS DIGITAL SECURITY | AUTOMATISMES ET SYSTEMES INDUSTRIELS | BIOMERIEUX SA | BNP PARIBAS ASSET MANAGEMENT BUSINESS FRANCE | CAPGEMINI | CARTIER JOAILLERIE | CEVA FREIGHT MANAGEMENT | CGI FRANCE | CMA CGM | CMA SHIPS | COCA COLA MIDI | COLAS TERRITOIRE SUD EST CARRIERES ET INDUSTRIE | CSTI INDUSTRIE | CT INGENIERIE | DATA RESPONS FRANCE | DE VIRIS | DESHONS HYDRAULIQUE | DGA TECHNIQUES NAVALES | DIAM France | EDF | EKIUM | FIVES MAINTENANCE | FORMAT VTC | FRAMATOME | FW TRANS | GOTOGAMES | GROUPE ATLANTIC | GXO LOGISTICS FROID France | HANSON UK | HARIBO RICQLES ZAN | HEINEKEN ENTREPRISE | HP FRANCE SAS | IPONE | IT LINK | LA FRANCAISE DES JEUX | LABORATOIRE D'HERBORISTRIE GENERALE | LABORATOIRE D'INFORMATIQUE ET SYSTEMES | LAPHAL INDUSTRIE | LOEWE | MICHELIN | MILHE ET AVONS | MIRION TECHNOLOGIES (MGPI) SAS | MSA France | MY KIWI | NATUREX SA | NAVAL GROUP | NESTLE NESPRESSO | NOVAEDIA | ORTEC | OUATECO | PANZANI | PEBEO | PERFECTSTAY | PIMAN GROUP | POPWORK | PRO BTP | PROCTER & GAMBLE FRANCE SAS | PROFILMAR | RECHERCHES TECHNIQUES DENTAIRES | RISINGSUD | SACOME | SANOFI AVENTIS R&D | SANTERNE MARSEILLE | SARTORIUS STEDIM BIOTECH | SARTORIUS STEDIM FMT | SCANIA FINANCE |SNCF | SNEF | SOCIETE DU GRAND PARIS | SOCOMEC SAS | SOMARSID | SOPRA STERIA GROUP | SUNTORY BEVRAGE & FOOD France | SWOOPIN | TALAN SOLUTIONS | TECHNICATOME | THALES GROUP | THALES SERVICES NUMERIQUES | TOTAL ENERGIES | TRACTEBEL ENGINEERING | TRIXELL | Vinci Énergies Systèmes d'Information | Vinovae | VISEO | WECLEEN | WELCO INDUSTRIES | XPERTISE SOLUTION | Ÿnsect
-
Project-based teaching
Since 1994, the Industrial Engineering and Computer Science (GII) program has incorporated professional training techniques into its teaching methods, based on real-life learning situations developed around different types of projects, each with very specific teaching objectives, where work is carried out in teams of 5 students. This pedagogical approach is subject to a continuous improvement process.
The course is made up of 60% "traditional" teaching (lectures, tutorials and practical work) and 40% projects. The proportion of projects in the training (from 24 to 50%) and the proportion of self-study in the projects (from 50 to 75%) vary increasingly from semester to semester.Practical training" projects (EP)
The aim is to solve problems whose scope is limited to theoretical teaching. Teams are put in the position of solving problems for which they do not necessarily have all the a priori knowledge, which forces them to adopt a self-learning approach. Each EP represents a workload of 16 hours over the course of a week. Teams are supervised by a teacher for 8 hours.
Micro-Projects (MP)
The aim is to solve complex problems (professional case studies) requiring the mobilization of all the knowledge of a Teaching Unit in a given field (Industrial Engineering, Automation or Computer Science). Teams are given a full week's full-time work (35 hours). They are required to submit a written document and give an oral presentation. Each team is supervised by a teacher for 4 hours.
Technical Achievement Projects (TRT)
The aim is to solve a complex problem by means of a technical achievement (hardware and software) in conjunction with a research team or a company. The TRT draws on all the technical, scientific and management knowledge and skills acquired during the course. They represent a workload of 200 hours per student, spread over 10 weeks in the fourth year. Each team is tutored by two teachers.
Industrial Application Work (TAI) projects
The aim is to solve a complex industrial problem involving all the dimensions of the course, and applying the technical and management skills of the Industrial and Computer Engineering profession. Each team is tutored by two teachers in collaboration with the industrialist who poses the problem. The TAI project takes place during semester 9 and represents a workload of 200 hours per student.
-
Courses
Students in our program take part in three compulsory internships, during which the skills acquired are assessed by the internship supervisor and the school's teaching staff.
- 3rd year: company discovery internship, 4 to 8 weeks, starting mid-June
- 4th year: introductory research internship (SIR) in an international laboratory, 12 weeks, starting mid-May
- 5th year: industrial development internship, 17 weeks minimum, starting in March.
A non-exhaustive list of companies (large corporations, ETIs, SMEs, start-ups) in which 5th year internships have taken place and led to employment is available in the "sector companies" tab.
The 4th year internships are supported by the GII program, AMU and institutional bodies for the award of grants.
List of universities that have hosted GII students over the past two years (31 destinations - 14 countries):
- Hochschule Bonn-Rhein-Sieg (Germany)
- Institute of Automatic Control (Germany)
- Bielefeld University of Applied Sciences (Germany)
- Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie (Germany)
- Universitat innsbruck (Austria)
- Université Libre de Bruxelles (Belgium)
- Polytechnique Montréal (Canada)
- Universidad Politecnica de Valencia (Spain)
- Universitat Polytecnica de Catalunya (Spain)
- University of Almería (Spain)
- University of Vigo (Spain)
- University of Iowa (USA)
- Technological University Dublin (Ireland)
- Department of Industrial Engineering, University of Florence (Italy)
- Politecnico di Bari (Italy)
- Politecnico di Milano (Italy)
- University of Cassino (Italy)
- Università degli Studi di Padova (Italy)
- Università di Genova (Italy)
- Noroff University College (Norway)
- NTNU - Norwegian University of Sciences and Technology (Norway)
- Delft University of Technology (Netherlands)
- University of Twente (Netherlands)
- Eindhoven University of Technology (Netherlands)
- University of Coimbra (Portugal)
- NOVA School of science and technology (Portugal)
- Nottingham Trent University (United Kingdom)
- Haute école de gestion de Genève (Switzerland)
- Istanbul Technical University (Turkey)
- Sabanci University (Turkey)
- Galatasaray University (Turkey)
These destinations are mainly drawn from the professional networks of GII teaching and research staff.
-
Professionalization contract
Our engineering students have the opportunity to complete their final year of the engineering cycle under a work-study contract with the following work-study schedule:
- September to January: Monday-Tuesday-Wednesday at school, Thursday-Friday at the company
- January to April: Monday-Tuesday at school, Wednesday-Thursday-Friday on the job
- From April: full-time at the company
Since the class of 2022, international mobility has been a requirement for the Polytech Marseille engineering diploma. It must be 12 weeks "cumulative post-baccalaureate", with a minimum of 4 consecutive weeks. The mobility options provided for in Polytech Marseille's study regulations are as follows:
- Study semester abroad
- Internships
- Employment
- Woofing
- Foreign students who have completed part of their studies in their home country.
- Gap year
Study semesters abroad
Semesters abroad, mainly in 4A and 5A (Semesters 7, 8 and mainly 9 and/or 10), are encouraged by the bilateral agreements (ERASMUS, Hors Europe, CIVIS, BRAFITEC...) linking the University, the School and our program with other foreign universities (Japan, Canada, Taiwan, South Korea, USA, Argentina, Brazil, Mexico, Chile, Belgium, Italy, Sweden, Germany, Spain...). In the "Industrial Engineering and Computer Science" stream, some of the universities that have already welcomed our students for a semester of study include:
- Frankfurt University of Applied Sciences (Germany)
- Cologne University of Applied Sciences (Germany)
- Universidade Estadual Paulista (Brazil)
- Université de Sherbrooke (Canada)
- École de Technologie Supérieure (Canada)
- University of Quebec (Canada)
- Universita de Guadalajara (Chile)
- Universita Catolica des Norte (Chile)
- Universidad de Valladolid (Spain)
- Universidad Politecnica de Cartagena (Spain)
- Politecnico di Milano (Italy)
- University of Salerno (Italy)
- Doshisha University (Japan)
- Stockholms universitet (Sweden)
Internships abroad
Among the three compulsory internships in the Industrial and Computer Engineering (ICE) program, the 4th-year research internship (SIR) must be carried out abroad in a world-class research laboratory. A list of the universities that have hosted GII students over the past two years (31 destinations - 14 countries) is available in the "Professionalization - Internship" section.
